Semi log plots ap precalculus – In the realm of mathematics, semi-log plots emerge as a captivating tool for visualizing data and revealing hidden patterns. Dive into the world of semi-log plots ap precalculus, where the interplay of linear and exponential trends unveils a fascinating narrative.
Semi-log plots, with their logarithmic scale on one axis, provide a unique perspective on data, making them invaluable in fields ranging from science to economics. Join us as we explore the intricacies of creating, interpreting, and applying these versatile graphical representations.
Definition and Purpose of Semi-Log Plots
Semi-log plots are a type of graphical representation that uses a logarithmic scale on one axis and a linear scale on the other. This type of plot is particularly useful for visualizing data that spans several orders of magnitude, making it easier to identify trends and patterns that might not be apparent on a linear-linear plot.
Semi-log plots are commonly used in various fields, including science, engineering, and finance. For example, they are often used to represent data on population growth, radioactive decay, and stock market trends.
Real-World Applications
- Population growth:Semi-log plots can be used to visualize the exponential growth of populations. The logarithmic scale on the y-axis allows for a wide range of values to be represented, while the linear scale on the x-axis shows the time period.
When you’re studying semi log plots in AP precalculus, it’s important to understand the basics of RGB color addition. For instance, if you add equal amounts of red, green, and blue light, you’ll get white light. You can find more information about RGB color addition at rgb color addition answer key . This will help you better understand how semi log plots work in AP precalculus.
- Radioactive decay:Semi-log plots are also useful for representing the exponential decay of radioactive isotopes. The logarithmic scale on the y-axis shows the activity of the isotope, while the linear scale on the x-axis represents time.
- Stock market trends:Semi-log plots can be used to visualize the exponential growth or decline of stock prices. The logarithmic scale on the y-axis allows for a wide range of values to be represented, while the linear scale on the x-axis shows the time period.
Creating Semi-Log Plots
Creating a semi-log plot involves several key steps. Firstly, it is important to determine which variable should be plotted on the logarithmic scale and which on the linear scale. Typically, the variable with a wider range of values or that exhibits exponential growth or decay is placed on the logarithmic scale.
Once the variables are assigned to their respective axes, the data needs to be scaled appropriately. The logarithmic scale is a non-linear scale, so the data values need to be transformed using the logarithmic function. The most common base for the logarithmic scale is 10, resulting in a common logarithm (log10).
The transformed data values are then plotted on the logarithmic axis.
When labeling the axes of a semi-log plot, it is important to clearly indicate that one axis is logarithmic. This can be done by adding the word “logarithmic” or “log” before the axis label. Additionally, the tick marks on the logarithmic axis should be spaced unevenly to reflect the non-linear nature of the scale.
Using a logarithmic scale for one axis has several advantages. Firstly, it allows for a wider range of values to be plotted on a single graph. Secondly, it can help to linearize exponential growth or decay patterns, making it easier to identify trends and relationships in the data.
However, it is important to note that using a logarithmic scale can also have some disadvantages. One disadvantage is that it can distort the visual representation of the data, making it difficult to compare values across different orders of magnitude.
Additionally, logarithmic scales can make it difficult to interpolate between data points, as the spacing between the tick marks is not uniform.
Overall, semi-log plots are a useful tool for visualizing data that exhibits exponential growth or decay. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of using a logarithmic scale, researchers and analysts can create informative and meaningful plots that effectively communicate their findings.
Interpreting Semi-Log Plots
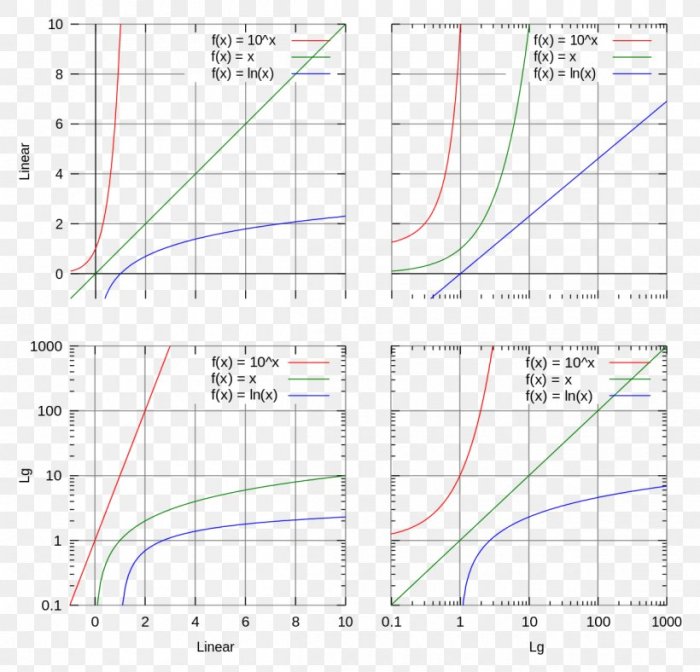
Semi-log plots offer valuable insights into the underlying patterns of data. Understanding the shape of the plot is crucial for interpreting the data effectively.
Linear Trends
A straight line in a semi-log plot indicates an exponential relationship between the variables. The slope of the line represents the exponential growth or decay rate.
If the line slopes upward, it signifies exponential growth. For example, a plot of population growth over time might show an upward-sloping line, indicating exponential population increase.
Conversely, a downward-sloping line indicates exponential decay. For instance, a plot of radioactive decay over time might display a downward-sloping line, representing the exponential decrease in the amount of radioactive material.
Exponential Growth/Decay
In addition to linear trends, semi-log plots can also reveal non-linear patterns. For example, a curve that bends upward indicates an accelerating growth rate, while a curve that bends downward suggests a decelerating decay rate.
Understanding the shape of a semi-log plot allows researchers and analysts to make informed decisions based on the data. It provides insights into the underlying relationships and trends, enabling them to draw meaningful conclusions and predictions.
Applications of Semi-Log Plots in Precalculus

Semi-log plots are useful tools in precalculus for analyzing and solving problems involving exponential and logarithmic functions.
Exponential functions are commonly encountered in precalculus, representing quantities that grow or decay at a constant percentage rate. By plotting these functions on a semi-log plot, we can visualize the exponential growth or decay and determine the rate of change.
Solving Logarithmic Equations, Semi log plots ap precalculus
Semi-log plots can also be used to solve logarithmic equations. By converting the equation to exponential form and plotting both sides on a semi-log plot, the solution can be determined graphically. The intersection point of the two curves represents the solution to the logarithmic equation.
Real-World Examples
Semi-log plots have practical applications in various fields, including:
- Population growth:Studying the growth of populations over time, which often follows an exponential pattern.
- Radioactive decay:Analyzing the decay of radioactive substances, which follows an exponential decay pattern.
- Chemical reactions:Modeling the rate of chemical reactions, which can be represented by exponential functions.
Limitations and Alternatives to Semi-Log Plots: Semi Log Plots Ap Precalculus
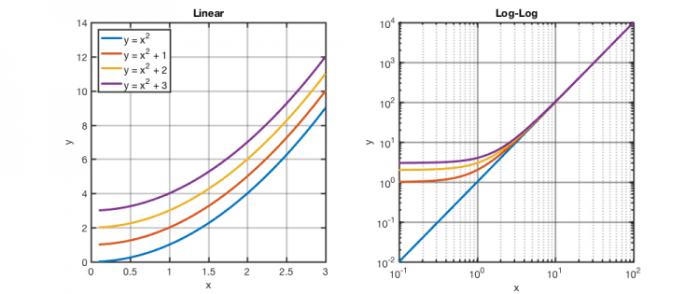
While semi-log plots are useful for certain types of data, they have limitations that can affect their accuracy and interpretability.
Distortion of Data at Low Values
One limitation of semi-log plots is that they can distort data at low values. This is because the logarithmic scale compresses the data, making it difficult to see small changes in values. As a result, semi-log plots may not be suitable for data that has a wide range of values, especially if the low values are important.
Alternatives to Semi-Log Plots
If the limitations of semi-log plots are a concern, there are alternative representations of data that can be considered.
Log-Log Plots
Log-log plots use a logarithmic scale for both the x-axis and the y-axis. This type of plot can be useful for data that has a wide range of values and for showing the relationship between two variables that are both proportional to each other.
Scatterplots
Scatterplots are a simple but effective way to visualize the relationship between two variables. They plot each data point as a point on a graph, and they can be used to identify trends and patterns in the data.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of a semi-log plot?
Semi-log plots are used to visualize data that exhibits exponential growth or decay, making it easier to identify trends and compare data sets.
How do I create a semi-log plot?
To create a semi-log plot, use a logarithmic scale on one axis (usually the y-axis) and a linear scale on the other axis. Plot the data points and connect them with lines or curves.
What are the advantages of using a semi-log plot?
Semi-log plots can compress large ranges of data, making it easier to see trends and compare data sets. They can also linearize exponential functions, making them easier to analyze.