Repaso Complete This Grammar Review is an essential tool for students, writers, and anyone who wants to improve their grammar skills. This comprehensive guide covers all the essential elements of grammar, from the parts of speech to sentence structure to punctuation and mechanics.
With clear explanations, engaging exercises, and additional resources, Repaso Complete This Grammar Review is the perfect way to master the fundamentals of grammar and take your writing to the next level.
This guide provides a thorough overview of the key elements of grammar, including the parts of speech, sentence structure, verb tenses, punctuation, and mechanics. It also includes practice exercises to help you reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered in the review.
In addition, the guide provides a list of additional resources for further study, including books, websites, and online courses.
Grammar Review Overview
A comprehensive grammar review is an essential tool for enhancing language proficiency. It provides a structured and systematic approach to reinforce grammatical concepts, identify areas for improvement, and expand vocabulary.
A comprehensive grammar review typically encompasses the following key elements:
Parts of Speech
Identifying and classifying words based on their grammatical function, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
Sentence Structure
Understanding the components of a sentence, including subjects, verbs, objects, and modifiers.
Tenses
Mastering the various verb tenses used to express time and aspect, such as present, past, and future.
Modals
Exploring the use of modal verbs to express possibility, necessity, and advice.
Conditionals
Understanding the different types of conditional sentences and their use in expressing hypothetical situations.
Passive Voice
Recognizing and using the passive voice to shift the focus of a sentence from the subject to the object.
Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are the different categories that words can be classified into based on their grammatical function and meaning. Identifying and understanding the parts of speech is essential for effective communication and language comprehension.
The main parts of speech include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech has its own set of rules and characteristics that determine how it is used in a sentence.
Nouns
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They can be proper nouns (specific names) or common nouns (general names). Examples of nouns include:
- Person: John, Mary, teacher
- Place: London, Paris, school
- Thing: book, car, house
- Idea: love, happiness, justice
Non-examples of nouns:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Quickly (adverb)
Verbs
Verbs are words that describe actions, states, or occurrences. They can be transitive (requiring an object) or intransitive (not requiring an object). Examples of verbs include:
- Action: run, jump, eat
- State: be, seem, appear
- Occurrence: happen, occur, take place
Non-examples of verbs:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Quickly (adverb)
Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They can provide information about the size, shape, color, quality, or other characteristics of a noun or pronoun. Examples of adjectives include:
- Big, small, tall
- Red, blue, green
- Good, bad, beautiful
Non-examples of adjectives:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Quickly (adverb)
Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They can provide information about the manner, time, place, or frequency of an action or event. Examples of adverbs include:
- Quickly, slowly, carefully
- Yesterday, today, tomorrow
- Here, there, everywhere
Non-examples of adverbs:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Red (adjective)
Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns or noun phrases. They can be personal pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), possessive pronouns (my, your, his, her, its, our, their), reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), or indefinite pronouns (one, anyone, everyone, nobody, something, anything, everything).
Examples of pronouns:
- I went to the store.
- The book is mine.
- He hurt himself.
- One should always be kind.
Non-examples of pronouns:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Red (adjective)
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. They can indicate location, direction, time, or other relationships. Examples of prepositions include:
- On, in, under
- To, from, towards
- At, by, until
Non-examples of prepositions:
- The (article)
- And (conjunction)
- Red (adjective)
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses. They can be coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet) or subordinating conjunctions (because, although, since, if, unless, while, until). Examples of conjunctions include:
- I went to the store and bought some milk.
- The weather was bad, so we stayed home.
- I will go to the park if it doesn’t rain.
Non-examples of conjunctions:
- The (article)
- Red (adjective)
- Quickly (adverb)
Interjections
Interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or reactions. They are often used independently of the rest of the sentence. Examples of interjections include:
- Wow!
- Oh no!
- Ouch!
Non-examples of interjections:
- The (article)
- Red (adjective)
- Quickly (adverb)
Sentence Structure
A sentence is a complete thought expressed in words. It has three basic components: a subject, a verb, and an object. The subject is the person or thing performing the action, the verb is the action being performed, and the object is the receiver of the action.
Types of Sentences
There are four main types of sentences: declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, and imperative.
- Declarative sentencesmake a statement. They end with a period.
- Interrogative sentencesask a question. They end with a question mark.
- Exclamatory sentencesexpress strong emotion. They end with an exclamation point.
- Imperative sentencesgive a command or request. They end with a period.
| Type | Purpose | Ending Punctuation |
|---|---|---|
| Declarative | Make a statement | Period |
| Interrogative | Ask a question | Question mark |
| Exclamatory | Express strong emotion | Exclamation point |
| Imperative | Give a command or request | Period |
Verb Tenses
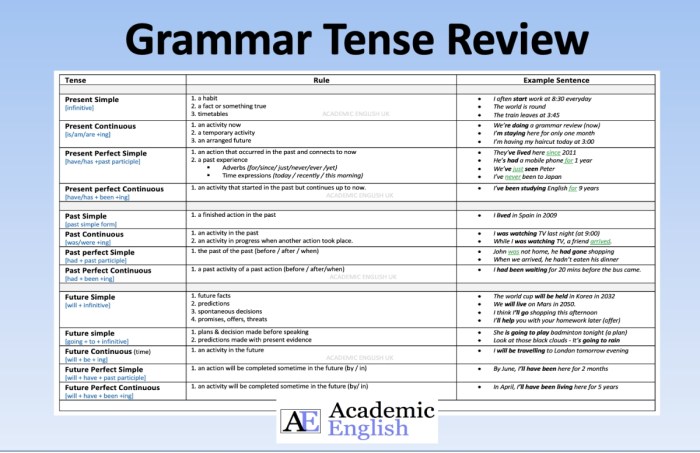
Verb tenses are grammatical forms that indicate the time of an action or event. They help us understand when something happened, is happening, or will happen.
In English, there are three main verb tenses:
- Present tense
- Past tense
- Future tense
Each tense has several different forms, which are used to express different aspects of time.
Present Tense
The present tense is used to describe actions or events that are happening now.
- Simple present: I eat breakfast every day.
- Present continuous: I am eating breakfast now.
- Present perfect: I have eaten breakfast.
- Present perfect continuous: I have been eating breakfast for an hour.
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe actions or events that happened in the past.
- Simple past: I ate breakfast yesterday.
- Past continuous: I was eating breakfast when you called.
- Past perfect: I had eaten breakfast before you arrived.
- Past perfect continuous: I had been eating breakfast for an hour when you arrived.
Future Tense
The future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future.
- Simple future: I will eat breakfast tomorrow.
- Future continuous: I will be eating breakfast at 8:00 AM.
- Future perfect: I will have eaten breakfast by the time you arrive.
- Future perfect continuous: I will have been eating breakfast for an hour by the time you arrive.
| Tense | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present simple | Describes actions or events that are happening now | I eat breakfast every day. |
| Present continuous | Describes actions or events that are happening at the moment of speaking | I am eating breakfast now. |
| Present perfect | Describes actions or events that started in the past and continue up to the present | I have eaten breakfast. |
| Present perfect continuous | Describes actions or events that started in the past and continue up to the present, with an emphasis on the duration of the action | I have been eating breakfast for an hour. |
| Past simple | Describes actions or events that happened in the past | I ate breakfast yesterday. |
| Past continuous | Describes actions or events that were happening at a specific time in the past | I was eating breakfast when you called. |
| Past perfect | Describes actions or events that happened before another action or event in the past | I had eaten breakfast before you arrived. |
| Past perfect continuous | Describes actions or events that started in the past and continued up to another action or event in the past, with an emphasis on the duration of the action | I had been eating breakfast for an hour when you arrived. |
| Future simple | Describes actions or events that will happen in the future | I will eat breakfast tomorrow. |
| Future continuous | Describes actions or events that will be happening at a specific time in the future | I will be eating breakfast at 8:00 AM. |
| Future perfect | Describes actions or events that will be completed by a specific time in the future | I will have eaten breakfast by the time you arrive. |
| Future perfect continuous | Describes actions or events that will have been happening for a specific duration by a specific time in the future | I will have been eating breakfast for an hour by the time you arrive. |
5. Punctuation and Mechanics: Repaso Complete This Grammar Review
Punctuation and mechanics are essential elements of written English, helping to convey meaning and clarity. Proper punctuation and capitalization facilitate comprehension, reduce ambiguity, and enhance the overall effectiveness of communication.
Punctuation Marks
Punctuation marks are symbols used to separate and clarify elements within a sentence. The most common punctuation marks include:
- Commas (,): Separate items in a series, introduce dependent clauses, and indicate pauses.
- Periods (.): End declarative and imperative sentences, as well as abbreviations.
- Question marks (?): Indicate the end of interrogative sentences.
- Exclamation points (!): Express strong emotions or emphasis.
- Colons (:): Introduce lists, explanations, or quotations.
- Semicolons (;): Separate independent clauses that are closely related.
- Quotation marks (“”): Enclose direct speech or quotations.
Capitalization
Capitalization is used to distinguish proper nouns (names of people, places, organizations, etc.) and the first word of a sentence. Proper capitalization enhances readability and clarity, as it helps readers identify specific entities and the beginning of sentences.
Hyphenation
Hyphenation is the process of dividing a word into syllables using a hyphen (-). It is commonly used to:
- Separate prefixes and suffixes from root words.
- Connect compound words.
- Break words at the end of a line.
Hyphenation aids in pronunciation, prevents confusion, and improves readability, especially in long or complex words.
Examples of Correct and Incorrect Punctuation and Mechanics
Correct:The students, who had studied diligently, passed the exam with flying colors. Incorrect:The students who had studied diligently, passed the exam with flying colors. Correct:Dr. Jane Smith, the renowned cardiologist, gave a lecture on heart health. Incorrect:dr.
jane smith, the renowned cardiologist, gave a lecture on heart health. Correct:The conference will be held on October 15th, 2023, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel. Incorrect:The conference will be held on October 15th 2023 at the Grand Hyatt Hotel.
Common Grammar Errors

Common grammar errors are often the result of a lack of understanding of the rules of grammar. These errors can make it difficult for readers to understand what you are trying to say and can damage your credibility as a writer.
There are a number of common grammar errors that people make. These include:
Subject-verb agreement
Subject-verb agreement means that the verb in a sentence must agree with the subject in number and person. For example, if the subject is singular, the verb must be singular. If the subject is plural, the verb must be plural.
There are a few rules that can help you to avoid subject-verb agreement errors:
- Identify the subject of the sentence.
- Determine whether the subject is singular or plural.
- Choose a verb that agrees with the subject in number and person.
Pronoun usage
Pronouns are words that take the place of nouns. There are a number of different types of pronouns, including personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, and demonstrative pronouns.
It is important to use pronouns correctly in order to avoid confusion. Here are a few tips for using pronouns correctly:
- Make sure that the pronoun agrees with the noun it replaces in number and gender.
- Use a possessive pronoun when you want to show that something belongs to someone.
- Use a demonstrative pronoun when you want to point out something.
Practice Exercises
Practice exercises are essential for reinforcing grammar concepts and developing proficiency in the language. These exercises provide opportunities for students to apply the rules and principles they have learned and to identify areas where they need additional support.
The exercises should be designed to cover a range of difficulty levels, from basic to advanced. This allows students to progress at their own pace and to challenge themselves as they improve their skills. Answer keys should be provided for self-assessment, so that students can monitor their progress and identify areas where they need to focus their efforts.
Types of Practice Exercises
- Fill-in-the-blank exercises:These exercises require students to fill in the blanks with the correct word or phrase. They can be used to practice a variety of grammar concepts, such as verb tenses, subject-verb agreement, and pronoun usage.
- Multiple-choice exercises:These exercises present students with a question and several possible answers. Students must choose the best answer from the options provided. Multiple-choice exercises can be used to assess students’ understanding of a wide range of grammar concepts.
- Sentence-writing exercises:These exercises require students to write sentences that demonstrate their understanding of a particular grammar concept. Sentence-writing exercises can be used to assess students’ ability to apply grammar rules in context.
- Error-correction exercises:These exercises present students with sentences that contain errors. Students must identify the errors and correct them. Error-correction exercises can help students to develop their proofreading skills and to identify common grammar mistakes.
Additional Resources

In addition to this grammar review, there are many other resources available to help you improve your grammar skills. These resources include books, websites, and online courses.
Some recommended resources include:
- Books:
- The Elements of Styleby William Strunk Jr. and E.B. White
- Grammar Girl’s Quick and Dirty Tips for Better Writingby Mignon Fogarty
- The Chicago Manual of Style
- Websites:
- Online courses:
Tools and Techniques for Improving Grammar Skills, Repaso complete this grammar review
In addition to using resources, there are a number of tools and techniques that you can use to improve your grammar skills. These include:
- Proofreading:Proofreading your work carefully can help you catch and correct any grammar errors.
- Using a grammar checker:Grammar checkers can help you identify and correct grammar errors in your writing.
- Practicing writing:The more you write, the better your grammar will become.
- Reading widely:Reading well-written material can help you improve your grammar and learn new words.
Q&A
What is Repaso Complete This Grammar Review?
Repaso Complete This Grammar Review is a comprehensive guide to grammar that covers all the essential elements, from the parts of speech to sentence structure to punctuation and mechanics.
Who is Repaso Complete This Grammar Review for?
Repaso Complete This Grammar Review is for anyone who wants to improve their grammar skills, including students, writers, and anyone else who wants to write more effectively.
What are the benefits of using Repaso Complete This Grammar Review?
Repaso Complete This Grammar Review can help you improve your grammar skills in a number of ways, including:
- Identifying and correcting common grammar errors
- Improving your sentence structure and punctuation
- Expanding your vocabulary
- Writing more clearly and effectively