With eukaryote vs prokaryote venn diagram at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
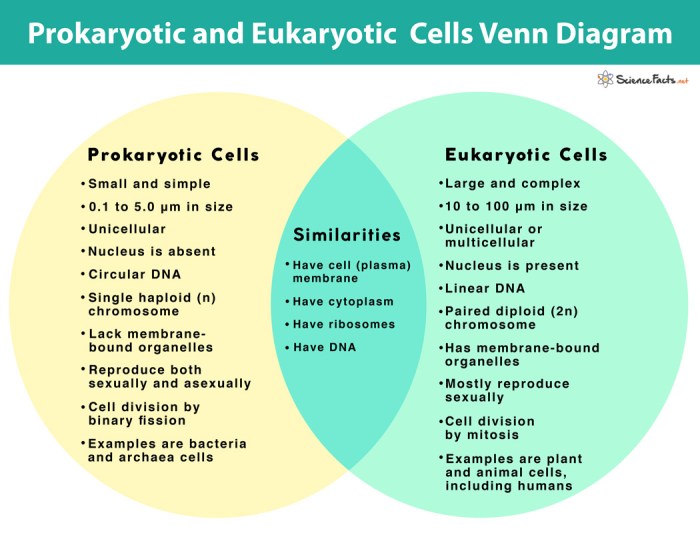
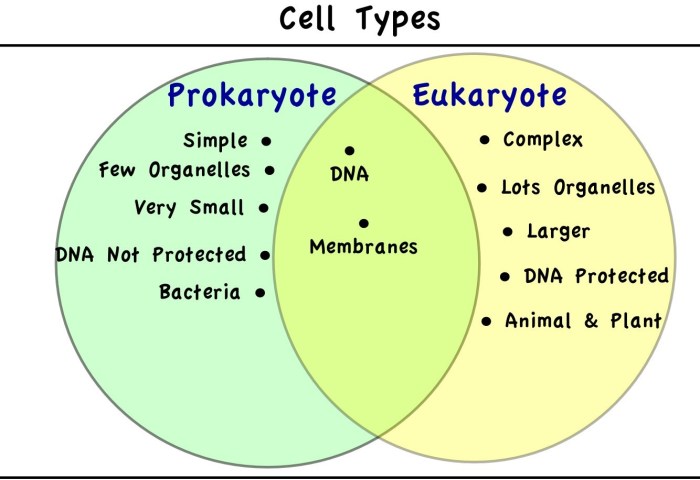
Key Differences between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes

Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are two fundamental types of cells that exhibit distinct structural and functional characteristics. The primary differences between them include the presence or absence of a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and the complexity of their genetic material.
Cell Structure
- Nucleus:Eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus, a membrane-bound compartment that houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA), while prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus.
- Organelles:Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, whereas prokaryotic cells lack these specialized structures.
- Genetic Material:Eukaryotic cells have their DNA organized into linear chromosomes within the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells have a single, circular chromosome.
Cell Division, Eukaryote vs prokaryote venn diagram
- Mitosis:Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis, a process that produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Meiosis:Eukaryotic cells also undergo meiosis, a process that produces four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Binary Fission:Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, a simple process that produces two identical daughter cells with the same genetic material as the parent cell.
Evolution
- Endosymbiotic Theory:The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between prokaryotic cells.
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts:According to the theory, mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells originated from ancient bacteria that were engulfed by a larger cell.
Applications
- Medicine:Eukaryotic cells are used in medical research and drug development, while prokaryotic cells are used in the production of antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals.
- Biotechnology:Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are used in genetic engineering and the production of recombinant proteins.
- Environmental Science:Prokaryotic cells play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and waste decomposition.
Commonly Asked Questions: Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote Venn Diagram
What is the key difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotes lack these features.
What is the role of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and is responsible for regulating gene expression.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission, a simple division of the cell into two identical daughter cells.