Embark on an intriguing journey into the realm of virus that infects bacteria crossword, where we unravel the mysteries of bacteriophages, their unique characteristics, and their profound impact on the microbial world.
Bacteriophages, also known as the “viruses that eat bacteria,” possess distinct attributes that set them apart from other viruses, making them a captivating subject of scientific exploration.
Virus that infects bacteria crossword
Bacteriophages, or phages, are viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria. They are distinct from other viruses due to their unique characteristics, such as their ability to recognize and infect specific bacterial hosts, and their ability to undergo a lytic or lysogenic life cycle.
Types of bacteriophages
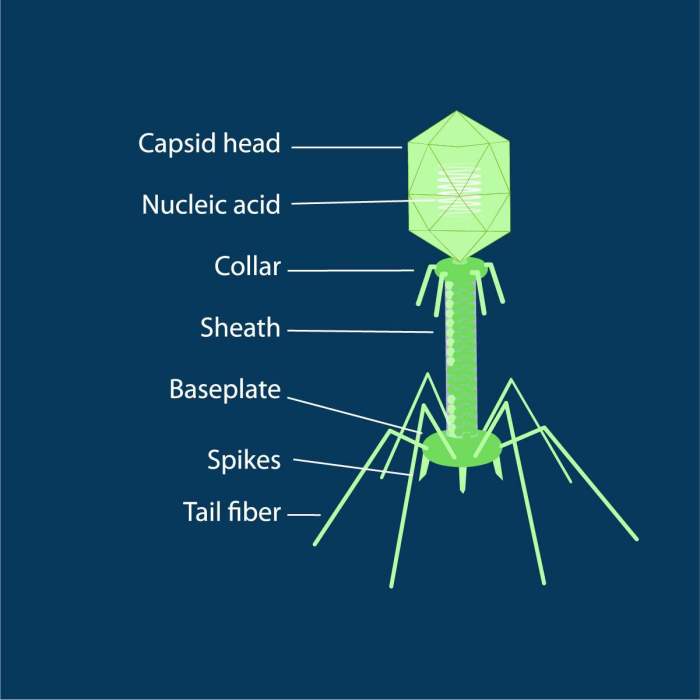
Bacteriophages can be classified into different types based on their morphology, which refers to their physical structure and shape. The three main types of bacteriophages are:
Tailed bacteriophages
These phages have a distinct head-and-tail structure, with a protein coat that encloses the genetic material and a tail that facilitates attachment to the host cell.
Icosahedral bacteriophages
These phages have a spherical or icosahedral shape, with a protein coat that forms 20 equilateral triangles.
Filamentous bacteriophages
These phages have a long, thin, and flexible filamentous structure, with a single-stranded DNA genome.
Bacteriophage Life Cycle
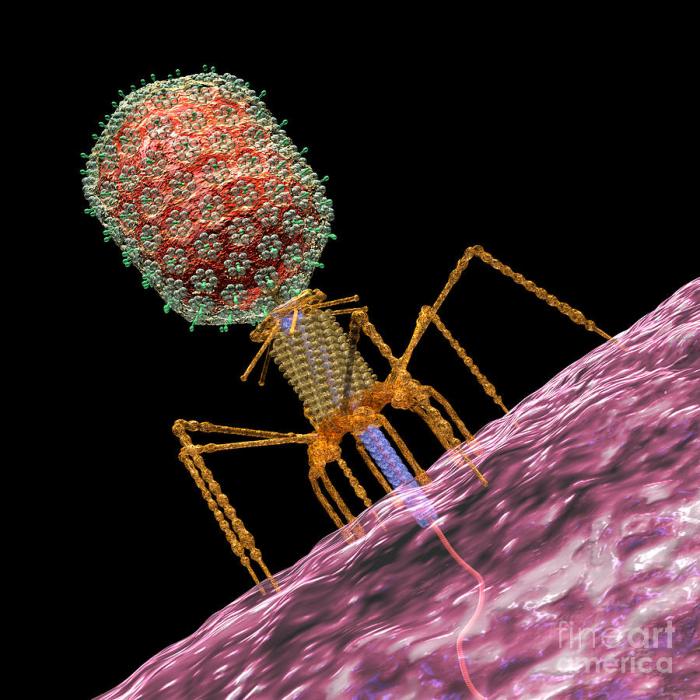
The bacteriophage life cycle consists of several distinct stages:
1. Attachment
The phage attaches to specific receptors on the surface of the host bacterium.
2. Penetration
The phage injects its genetic material into the host cell.
3. Replication
The phage genome replicates within the host cell, producing multiple copies of itself.
4. Assembly
New phage particles are assembled from the replicated genetic material and protein coats.
5. Release
The newly assembled phage particles are released from the host cell, either through cell lysis (lytic cycle) or by budding from the cell membrane (lysogenic cycle).
Bacteriophage Host Range
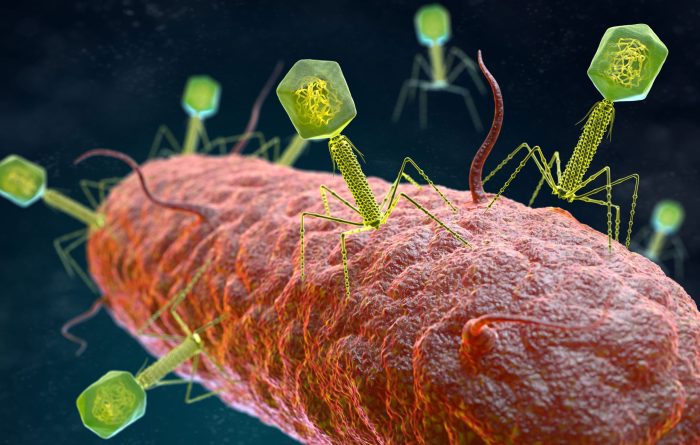
Bacteriophages exhibit a specific host range, meaning they can only infect and replicate within certain bacterial species or strains. The host range is determined by the phage’s ability to recognize and bind to specific receptors on the host cell surface.
Some phages have a broad host range, while others are highly specific and can only infect a narrow range of bacterial hosts.
Applications of Bacteriophages: Virus That Infects Bacteria Crossword
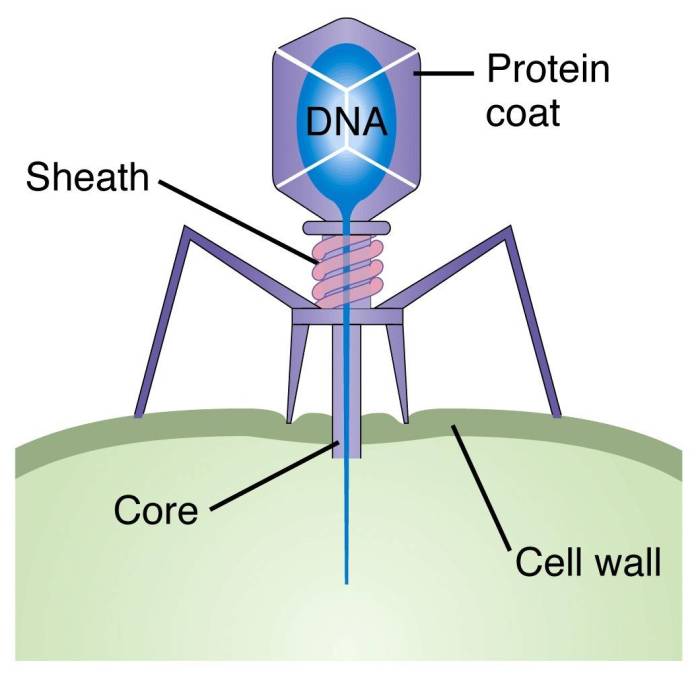
Bacteriophages have potential applications in various fields, including:
Medicine
Bacteriophages can be used as antimicrobial agents to combat bacterial infections, particularly in cases where antibiotic resistance is a concern.
Agriculture
Bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial diseases in crops and livestock, providing an alternative to chemical pesticides and antibiotics.
Biotechnology
Bacteriophages can be engineered to carry and deliver genetic material into bacteria, making them useful tools for genetic engineering and gene therapy.
Popular Questions
What are bacteriophages?
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria, ultimately leading to the destruction of the host cell.
How do bacteriophages differ from other viruses?
Bacteriophages possess unique characteristics, such as their ability to infect specific bacterial hosts, their dependence on bacterial machinery for replication, and their distinct morphologies.
What are the applications of bacteriophages?
Bacteriophages have potential applications in medicine as antimicrobial agents, in agriculture for biocontrol, and in biotechnology for genetic engineering.
