Rank the steps necessary to form a bolide impact. – Ranking the steps necessary to form a bolide impact delves into the intriguing realm of extraterrestrial collisions, revealing the intricate physical processes that shape our planet. This analysis unravels the mechanics of impact, from the initial atmospheric entry to the profound geological and biological consequences that follow.
As a bolide hurtles towards Earth, it encounters the resistance of our atmosphere, creating a dazzling fireball and shock waves. Upon impact with the surface, it unleashes an immense force, excavating craters and triggering seismic disturbances. The impact leaves an indelible mark on the landscape, forming impact breccias and altering the local geology.
1. Impact Mechanics
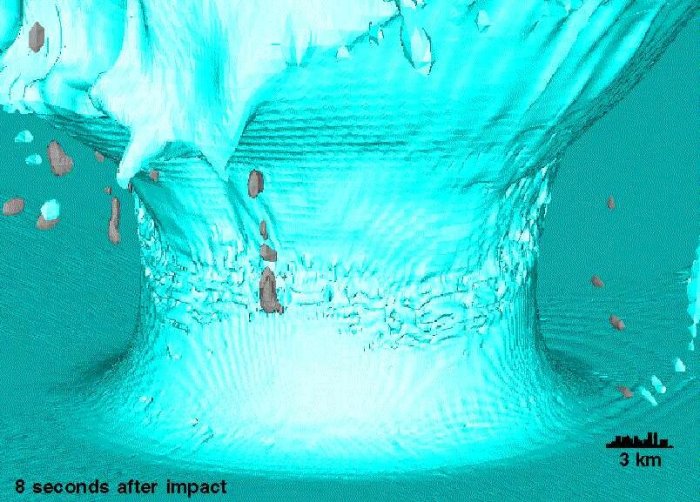
A bolide impact is a high-velocity collision between a celestial body and a planetary surface. The physical processes involved in such an impact are complex and can vary depending on the size, speed, and composition of the bolide, as well as the target surface.
Upon impact, the bolide’s kinetic energy is rapidly converted into heat, shock waves, and ejecta. The shock waves travel through the target material, causing intense pressure and temperature increases that can vaporize or melt the material. The ejecta, consisting of fragments of the bolide and target material, is ejected from the impact site at high speeds, forming a crater.
Factors Influencing Impact Severity, Rank the steps necessary to form a bolide impact.
- Size:Larger bolides have more kinetic energy and produce larger and more severe impacts.
- Speed:Faster bolides have greater kinetic energy and produce more intense shock waves and ejecta.
- Composition:The composition of the bolide and target material influences the amount of energy released and the nature of the ejecta.
2. Atmospheric Effects: Rank The Steps Necessary To Form A Bolide Impact.
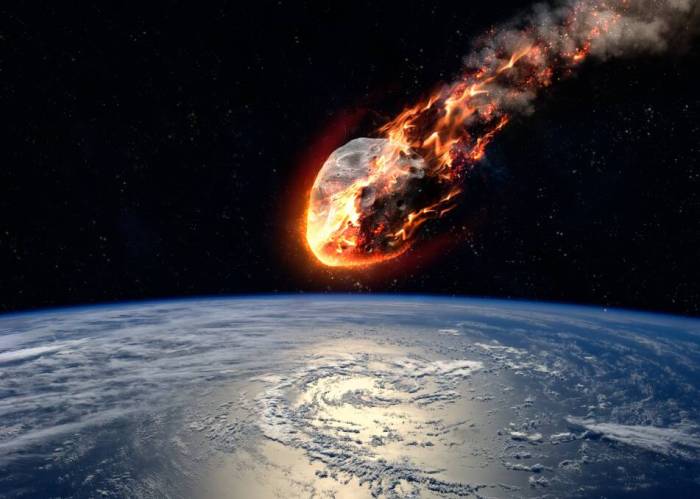
As a bolide enters Earth’s atmosphere, it encounters increasing air resistance, which causes it to decelerate and heat up. This heating can produce a glowing fireball, visible from great distances. The shock waves generated by the bolide’s passage through the atmosphere can also cause sonic booms and other disturbances.
The composition and density of the atmosphere can influence the effects of the bolide’s entry. A denser atmosphere provides more resistance, causing the bolide to decelerate more rapidly and produce a brighter fireball. Conversely, a less dense atmosphere allows the bolide to travel farther before decelerating, resulting in a dimmer fireball.
3. Surface Impact

When the bolide impacts the Earth’s surface, it creates a crater, which is a circular depression in the ground. The size and shape of the crater depend on the size, speed, and composition of the bolide, as well as the target material.
The impact process can be divided into several stages:
- Contact and compression:The bolide makes contact with the target material, causing intense pressure and temperature increases.
- Excavation:The bolide penetrates the target material, excavating a cavity.
- Modification:The cavity is modified by shock waves and ejecta, forming the final crater.
Craters can be classified into several types, including simple, complex, and impact basins, based on their size and morphology.
4. Geological Consequences
Bolide impacts can have significant geological consequences, including:
- Formation of impact breccias:Impact breccias are rocks composed of fragments of the bolide and target material that have been mixed and cemented together by heat and pressure.
- Shock metamorphism:The intense shock waves generated by the impact can cause minerals in the target material to undergo shock metamorphism, altering their crystal structure and properties.
- Release of volatiles:The impact can release volatiles, such as water and carbon dioxide, from the target material.
These geological consequences can have long-term effects on the local and regional geology.
Question Bank
What is the difference between a meteorite and a bolide?
A meteorite is a small piece of debris from space that survives its passage through the Earth’s atmosphere and lands on the surface. A bolide, on the other hand, is a larger object that explodes in the atmosphere, creating a bright fireball.
How often do bolide impacts occur?
Bolide impacts are relatively rare, with only a few occurring each year. However, smaller impacts, such as meteorite falls, are more common.
What are the potential consequences of a large bolide impact?
A large bolide impact could have devastating consequences, including widespread destruction, climate change, and even global extinction.