Judicial branch in a flash teacher guide – Judicial Branch in a Flash: A Comprehensive Guide for Teachers unravels the intricacies of the American judicial system, empowering educators with the knowledge to captivate their students. This guide delves into the structure, functions, and impact of the judicial branch, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential pillar of American government.
Through engaging explanations and real-world examples, this guide illuminates the role of the judicial branch in safeguarding individual rights, interpreting the Constitution, and ensuring the rule of law. Its accessible language and clear organization make it an invaluable resource for teachers seeking to instill a deep understanding of the judicial process in their classrooms.
Role of the Judicial Branch
The judicial branch of the US government plays a crucial role in interpreting and upholding the law, protecting individual rights, and resolving disputes. Its primary functions include:
- Interpreting the Constitution and Laws:The judicial branch determines the meaning and application of the Constitution and federal laws, ensuring that government actions align with these legal frameworks.
- Resolving Disputes:Courts adjudicate legal disputes between individuals, organizations, and the government, providing a fair and impartial forum for resolving conflicts.
- Protecting Individual Rights:The judicial branch safeguards the fundamental rights and liberties of citizens, as Artikeld in the Bill of Rights and other constitutional amendments.
- Checking the Other Branches:Through the principle of judicial review, the judicial branch can declare laws and actions of the executive and legislative branches unconstitutional, ensuring a balance of power among the three branches of government.
Judicial independence is paramount to the effective functioning of the judicial branch. Judges are appointed for life, insulated from political pressures, and bound by ethical codes to ensure impartial and unbiased decision-making.
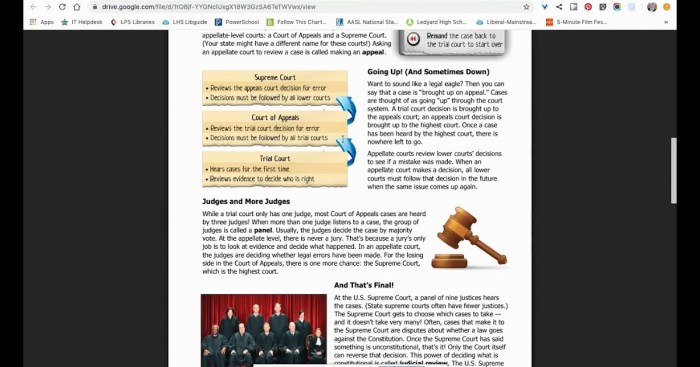
Structure of the Judicial Branch

The US judicial system is a hierarchical structure, with federal and state courts operating at different levels:
- Federal Courts:These courts have jurisdiction over cases involving federal laws, the Constitution, and disputes between states or the federal government and individuals.
- State Courts:These courts handle cases involving state laws and disputes within state boundaries.
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land and has the final say on legal matters. It reviews cases from lower courts and issues binding decisions that shape US law and legal precedent.
Judges to the federal judiciary are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate. This process ensures that judges are qualified, experienced, and meet the ethical standards required for serving on the bench.
Judicial Process: Judicial Branch In A Flash Teacher Guide
A typical legal case involves several steps:
- Filing a Complaint:The plaintiff initiates the case by filing a complaint outlining their claims against the defendant.
- Discovery:Both parties exchange information and evidence to prepare for trial.
- Trial:The case is presented before a judge or jury, who determine the facts and apply the law to reach a verdict.
- Judgment:The court issues a judgment based on the verdict, which may include remedies such as damages or injunctions.
- Appeals:Either party may appeal the judgment to a higher court if they believe errors were made.
Judges preside over trials, ensure fairness and adherence to legal procedures, and instruct juries on the applicable law.
Juries, composed of citizens, determine the facts of the case and render verdicts based on the evidence presented.
Attorneys represent clients, present evidence, and argue legal positions in court.
Various types of evidence can be presented in court, including witness testimony, documents, and physical evidence.
Judicial Opinions

Judicial opinions are written explanations of court decisions that provide the rationale for the court’s judgment.
- Majority Opinion:The opinion of the majority of judges on the court, which sets forth the legal basis for the decision.
- Dissenting Opinion:The opinion of judges who disagree with the majority, outlining their reasoning and alternative views.
- Concurring Opinion:The opinion of judges who agree with the majority’s decision but offer additional or different reasoning.
Landmark judicial opinions have significantly shaped US law and jurisprudence. Examples include:
- Marbury v. Madison(1803): Established the principle of judicial review.
- Brown v. Board of Education(1954): Declared racial segregation in schools unconstitutional.
- Roe v. Wade(1973): Recognized the constitutional right to abortion.
Impact of the Judicial Branch

The judicial branch plays a profound role in American society:
- Protecting Individual Rights:The judicial branch safeguards the fundamental rights and freedoms of citizens, ensuring equality, justice, and the rule of law.
- Promoting Social Change:The judicial branch has played a pivotal role in advancing social progress, such as the desegregation of schools, the expansion of voting rights, and the recognition of same-sex marriage.
- Interpreting the Constitution:The judicial branch is the ultimate arbiter of the meaning of the Constitution, ensuring that laws and government actions conform to its principles.
By upholding the rule of law and protecting individual rights, the judicial branch serves as a cornerstone of American democracy and ensures the fair and just administration of justice.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary function of the judicial branch?
The primary function of the judicial branch is to interpret the law, resolve disputes, and ensure justice.
How many levels of courts are there in the US judicial system?
There are three levels of courts in the US judicial system: federal courts, state courts, and local courts.
What is the role of the Supreme Court?
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the US and has the final say on matters of law.

