Get ready to conquer Chapter 8 of your AP Statistics exam with our comprehensive guide to chapter 8 ap stats test answers. We’ll dive into the key concepts, question types, and strategies to help you achieve success.
This chapter covers hypothesis testing, sampling distributions, confidence intervals, sample size determination, and power analysis. Each topic is explained clearly and concisely, with real-world examples to illustrate their practical applications.
Chapter 8 AP Stats Test Content: Chapter 8 Ap Stats Test Answers
Chapter 8 of the AP Statistics curriculum focuses on confidence intervals and hypothesis testing. Confidence intervals provide a range of plausible values for a population parameter, while hypothesis testing allows us to make inferences about the population based on sample data.
Some of the key concepts covered in this chapter include:
- Confidence intervals for means, proportions, and variances
- Hypothesis testing for means, proportions, and variances
- Type I and Type II errors
- Power of a hypothesis test
On the AP Statistics test, you may encounter questions that require you to:
- Calculate confidence intervals for means, proportions, and variances
- Conduct hypothesis tests for means, proportions, and variances
- Interpret the results of confidence intervals and hypothesis tests
- Evaluate the power of a hypothesis test
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether there is enough evidence to reject a null hypothesis (H 0) in favor of an alternative hypothesis (H 1). The null hypothesis represents the claim that there is no significant difference or relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis suggests that there is a difference or relationship.
Hypothesis testing involves several steps:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Set the significance level (α).
- Collect data and calculate the test statistic.
- Determine the p-value.
- Make a decision: reject or fail to reject H 0.
Examples of Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is widely used in various fields:
- Medical research:Testing the effectiveness of new treatments.
- Marketing:Evaluating the impact of advertising campaigns.
- Social sciences:Examining the relationship between variables such as education and income.
Sampling Distributions
In hypothesis testing, we often need to make inferences about a population based on a sample. However, since samples vary from one another, we cannot rely on a single sample to provide an accurate representation of the population. Sampling distributions help us overcome this challenge by providing a theoretical framework for understanding the distribution of sample statistics.
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of a sample statistic (such as the sample mean or sample proportion) that is obtained from all possible samples of a given size from a population. It shows the possible values that the sample statistic can take and the probability of each value occurring.
Types of Sampling Distributions
- Sampling distribution of the mean:The sampling distribution of the mean is the probability distribution of the sample means that would be obtained from all possible samples of a given size from a population. It is approximately normal if the sample size is large enough (by the Central Limit Theorem), regardless of the shape of the population distribution.
- Sampling distribution of the proportion:The sampling distribution of the proportion is the probability distribution of the sample proportions that would be obtained from all possible samples of a given size from a population. It is approximately normal if the sample size is large enough and the population proportion is not too close to 0 or 1.
Using Sampling Distributions to Make Inferences
Sampling distributions allow us to make inferences about a population based on a sample. By knowing the sampling distribution of a sample statistic, we can determine the probability of obtaining a sample statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the one we observed.
This information can then be used to make a decision about the null hypothesis.
If you’re struggling with chapter 8 AP stats test answers, you’re not alone. Fortunately, there are resources available to help you succeed. Consider checking out ben caldwell law and ethics ceu for guidance on the subject. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep working at it and you’ll master chapter 8 AP stats test answers in no time.
For example, if we observe a sample mean that is much larger than the population mean, we can use the sampling distribution of the mean to determine the probability of obtaining such a large sample mean if the null hypothesis is true.
If this probability is very small, then we can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the population mean is actually larger than the hypothesized value.
Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals are statistical tools used to estimate population parameters, such as the mean or proportion, based on sample data. They provide a range of plausible values for the population parameter with a certain level of confidence.
The construction of a confidence interval involves several steps:
- Determine the sample statistic:Calculate the mean, proportion, or other relevant statistic from the sample data.
- Find the standard error:Estimate the standard deviation of the sampling distribution using the sample data.
- Choose a confidence level:Select the desired level of confidence, such as 95% or 99%, which determines the width of the interval.
- Calculate the margin of error:Multiply the standard error by the critical value obtained from the t-distribution or standard normal distribution, depending on the sample size.
- Construct the confidence interval:Add and subtract the margin of error from the sample statistic to obtain the lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval.
Confidence intervals are used in various applications, such as:
- Estimating the population mean based on a sample mean, with a specified margin of error.
- Determining the population proportion within a specified confidence level.
- Testing hypotheses about population parameters by comparing the confidence interval to a hypothesized value.
Sample Size Determination
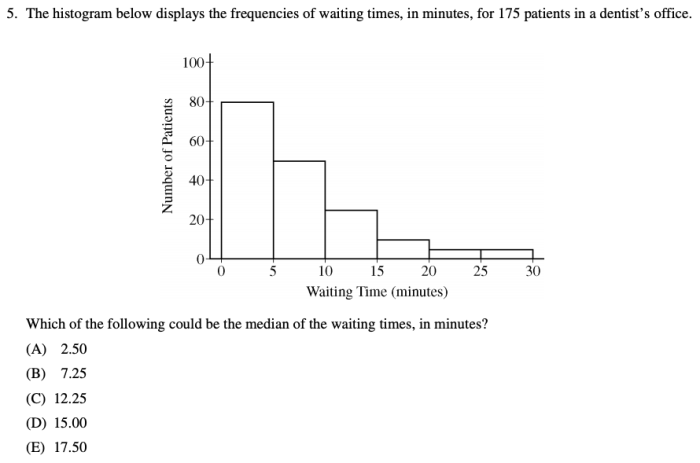
Determining the appropriate sample size is crucial for statistical studies to ensure reliable and accurate results. Several factors influence sample size determination, including the desired level of confidence, the margin of error, and the population variability.
Methods used to determine sample size include using formulas based on statistical theory, consulting statistical tables, or utilizing software packages that perform sample size calculations.
Confidence Level and Margin of Error
The confidence level represents the level of certainty in the results. A higher confidence level requires a larger sample size. The margin of error refers to the amount of error that is acceptable in the results. A smaller margin of error requires a larger sample size.
Population Variability
The variability of the population being studied also affects sample size determination. A more variable population requires a larger sample size to obtain a representative sample.
Example
A researcher wants to estimate the average income of a population with a 95% confidence level and a margin of error of $100. The researcher estimates the population standard deviation to be $500. Using a formula, the researcher calculates that a sample size of 256 is required.
Power Analysis

Power analysis is a statistical technique used to determine the probability of finding a statistically significant result in a hypothesis test. It helps researchers design studies that are likely to produce meaningful results and avoid false negatives.
Factors Influencing Power
The power of a study is influenced by several factors, including:
- Sample size: Larger sample sizes increase the power of a study.
- Effect size: Studies with larger effect sizes are more likely to find statistically significant results.
- Significance level: Using a more stringent significance level (e.g., 0.01 instead of 0.05) decreases the power of a study.
Examples of Power Analysis, Chapter 8 ap stats test answers
Power analysis is used in various fields to design effective studies. Here are a few examples:
- In medical research, power analysis helps determine the sample size needed for a clinical trial to have a high probability of detecting a treatment effect.
- In psychology, power analysis aids in determining the number of participants required for a study to have a good chance of finding a statistically significant difference between two groups.
- In business research, power analysis assists in determining the sample size for a survey to ensure that the results are reliable and have a low risk of sampling error.
Additional Resources
Preparing for the Chapter 8 AP Statistics test requires dedication and a comprehensive approach. To assist you in your preparation, we have compiled a list of valuable resources that will enhance your understanding of the key concepts and provide ample practice opportunities.
Practice Questions and Study Guides
Khan Academy
Offers a comprehensive set of practice questions and video tutorials covering all the topics in Chapter 8.
Varsity Tutors
Provides detailed study guides, practice tests, and expert-led video lessons.
College Board
The official AP Statistics website offers sample questions, practice exams, and other resources.
Online Courses and Tutorials
edX
Offers a free online course on AP Statistics that covers the entire curriculum.
Coursera
Provides interactive tutorials and quizzes on hypothesis testing, sampling distributions, and confidence intervals.
YouTube
Numerous channels offer video tutorials and explanations of Chapter 8 concepts.
Other Helpful Resources
AP Statistics Forum
A community forum where students can ask questions, share tips, and collaborate with peers.
Statistics and Probability Problems
A website that provides a vast collection of practice problems and solutions.
NIST Engineering Statistics Handbook
A comprehensive reference guide for statistical methods and applications.By utilizing these resources, you can supplement your classroom learning, reinforce your understanding, and build confidence in your ability to excel on the Chapter 8 AP Statistics test.
Expert Answers
What types of questions can I expect on the Chapter 8 AP Stats test?
The test may include multiple-choice questions, free-response questions, and short answer questions covering all the concepts discussed in Chapter 8.
How can I prepare for the hypothesis testing section?
Practice identifying the null and alternative hypotheses, understanding the steps involved in hypothesis testing, and interpreting the results.
What is the importance of sampling distributions?
Sampling distributions help us make inferences about a population based on a sample. They allow us to estimate the variability of sample statistics and determine the probability of obtaining a particular sample result.